There are numerous threads
that can be found on “xp_delete_file” regarding various issues when used in a Maintenance
Plan in SQL Server to remove old database backup (bak) or transaction backup (trn)
from the disk and folder. This is a built-in and undocumented extended stored
procedure and used internally by the Maintenance Plan Wizard. This Extended
Stored Procedure can also be executing manually in SSMS such as:
declare @filedate datetime
set @filedate = getdate() - 5
execute master.dbo.xp_delete_file 0, 'd:\temp\', 'bak', @filedate, 1
Issues:
We
often find that the maintenance task fails with the following error message in
ERROR Log and SQL Agent Job history respectively. In addition to the message, we
will also see mini-dump in the SQL Server log folder.
Error: 18002, Severity: 20, State: 1.
Exception happened when running extended stored procedure
'xp_delete_file' in the library 'xpstar.dll'. SQL Server is terminating process
73. Exception type: Win32 exception; Exception code: 0xc0000005.
Source: Maintenance Cleanup Task Execute SQL Task Description:
Executing the query "EXECUTE master.dbo.xp_delete_file 0, N'd:\temp', N'trn',
N'2010-01-21T13:00:00' " failed with the following error: "A severe
error occurred on the current command. The results, if any, should be
discarded. A severe error occurred on the current command. The results, if any,
should ... The package execution fa... The step failed.
If
we run “xp_delete_file” manually in SSMS, we may see the following error
message:
Msg 0, Level 11, State 0, Line 0
A severe error occurred on the current command. The results, if any, should be discarded.
Msg 0, Level 20, State 0, Line 0
A severe error occurred on the current command. The results, if any, should be discarded.
Alternative to “xp_delete_file”:
As
this functionality has some known issues and consequences, it is wise to use
PowerShell script as an alternative. Following
are a few examples on how to remove older “bak” or “trn” files from a folder as
well as from sub-folder. This PowerShell Script can be used to delete any kind
of files from disk.
Example One (based on number of
days):
Remove
database backup files with the extension “bak” which are longer than 5 days
old.
# target path
$TargetPath =
"d:\temp\"
# files to delete more than 5 days
$Days = 5
# extension of the file to delete
$Extension = "*.bak"
$CurrentDate =
Get-Date
$LastWrite = $CurrentDate.AddDays(-$days)
# Get files based on lastwrite filter in the
specified folder
$FilesToDeletes =
Get-Childitem $targetpath
-Include $Extension -Recurse | Where {$_.LastWriteTime -le "$LastWrite"}
foreach ($File in $FilesToDeletes)
{
if ($File -ne $NULL)
{
Remove-Item $File.FullName | out-null
}
}
Example Two (based on number
of hours):
Remove
transaction log backup files with the extension “trn” which are longer than 10
hours old.
# target path
$TargetPath =
"d:\temp\"
# files to delete more than 10 hours
$Hours = 10
# extension of the file to delete
$Extension = "*.trn"
$CurrentDate =
Get-Date
$LastWrite = $CurrentDate.AddHours(-$Hours)
# Get files based on lastwrite filter in the
specified folder
$FilesToDeletes =
Get-Childitem $targetpath
-Include $Extension -Recurse | Where {$_.LastWriteTime -le "$LastWrite"}
foreach ($File in $FilesToDeletes)
{
if ($File -ne $NULL)
{
Remove-Item $File.FullName | out-null
}
}
Using PowerShell script in
SQL Agent Job (SQL 2008+):
Using
PowerShell Script in SQL Server Agent Job is simple. Follow the steps described
below:
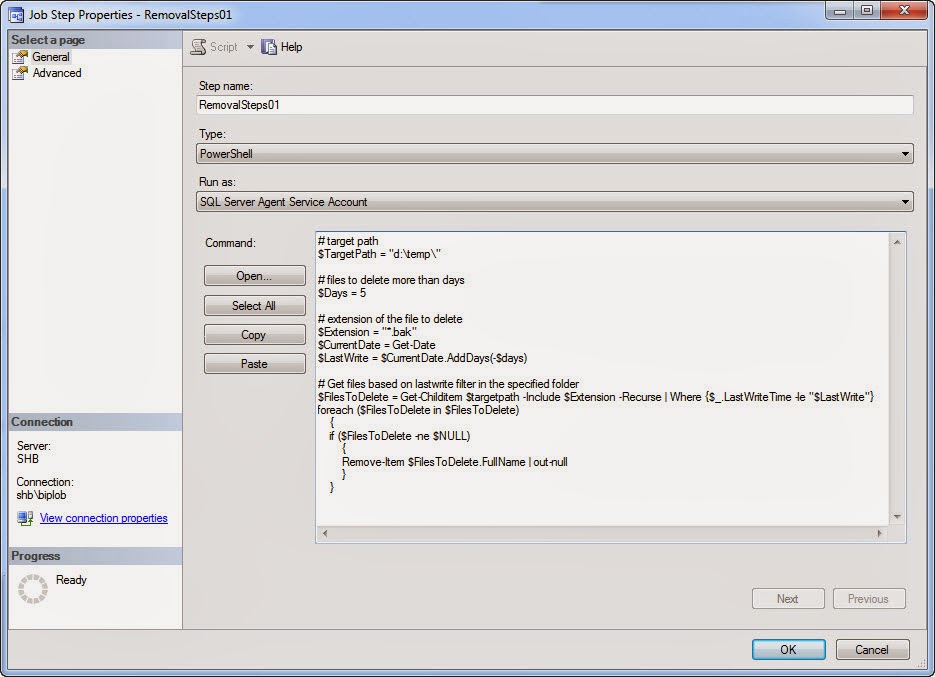
1. Create a new SQL Agent Job, for
example “Remove_older_BAK_files”.
2. “In the Job Step properties”
– select “PowerShell” as a type (figure #1).
3. Paste the PowerShell script.
Don’t forget to adjust your path and day parameter according to your need.
4. Exit by saving the job and
then execute it.
If
you want to use the above job in a Maintenance Plan, you can use “SQL Server
Agent Job Task” as shown below (figure #2).
Figure #1: SQL Agent Job with PowerShell
Script:

No comments:
Post a Comment