In many RDBMS there is a split_part()
function which is used to split a string into multiple parts based on a
delimiter and return a specific part of the split result. Generally, it takes
three arguments: the input string, the delimiter, and the position of the
desired part, start from the left of the string.
In SQL Server, there are no such direct function
exists, however there is a function called string_split which can be used to
achieve the same result.
Let’s
say we want to extract a specific nth delimited substring from a string which
are stored in a column, and let’s consider the following SQL Code to create
delimited column for demonstration purpose.
CREATE TABLE #tmp ( lname VARCHAR(256) )
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'How,will,we,use,our,increasing,scientific,knowledge' AS lname
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'He,has,a,limited,knowledge,of,English' AS lname
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'The,owner,claims,the,boat,was,being,used,without,her,knowledge' AS lname
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'Applicants,should,have,a,working,knowledge' AS lname
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'judging,from,my,personal,experience,and,information' AS lname
INSERT #tmp SELECT 'Such,situations,require,fundamental,knowledge ' AS lname
SELECT * FROM #tmp
T-SQL
Solution:
To
extract the nth delimited substring from the column “lname”, we can use the CROSS
APPLY along with the string_split function. If we want to extract 3rd substring
from the “lname” column, we can simply write the following T-SQL code:
SELECT t.lname,
sp.value AS lextract
FROM #tmp AS t
CROSS apply string_split(t.lname, ',', 1) AS sp
WHERE ordinal = 3
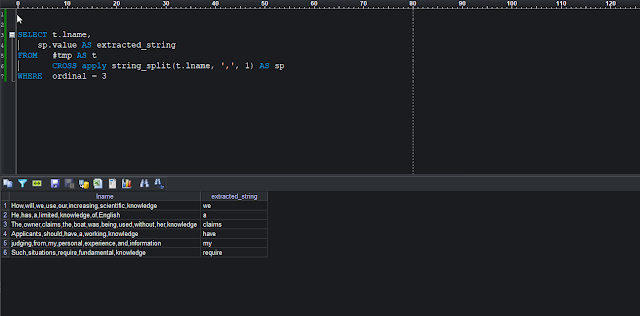 |
Using CROSS APPLY with string_split buit-in function
|
If
we want extract 6th delimited substring, then we need to simply use the ordinal value equal
to 6, for example:
SELECT t.lname,
sp.value AS lextract
FROM #tmp AS t
CROSS apply string_split(t.lname, ',', 1) AS sp
WHERE ordinal = 6
Creating
a split_part function from starting SQL Server 2016:
We
can create a similar function such as PostgreSQL or Snowflake in SQL Server, which can
be used in similar way.
CREATE FUNCTION split_part(@string VARCHAR(256) ,@delimiterchar VARCHAR(5) ,@npart TINYINT)
RETURNS VARCHAR(256)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @value VARCHAR(256)
SELECT @value=value FROM string_split(@string ,@delimiterchar ,1) WHERE ordinal = @npart
RETURN (@value)
END
-- Calling the split_part function:
SELECT master.dbo.split_part(lname, ',', 3) FROM #tmp
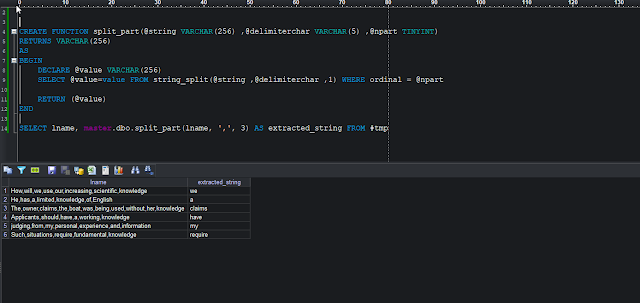 |
Using a custom function split_part
|
Creating
split_part using XML functionality – will work from SQL 2005:
CREATE FUNCTION split_part(@Input VARCHAR(256), @delimiterchar VARCHAR(5), @nPart TINYINT)
RETURNS VARCHAR(256)
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @XML XML;
DECLARE @value VARCHAR(256);
SET @XML = CAST('<x>' + REPLACE(@Input, @delimiterchar,'</x><x>') + '</x>' AS XML);
WITH StringSource([rowID], [rowValue]) AS
(
SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY T.c ASC),
T.c.value('.' ,'VARCHAR(256)')
FROM @XML.nodes('./x') AS T(c)
)
SELECT @value = [rowValue] FROM StringSource
WHERE [rowID] = @nPart;
RETURN(@value)
END
-- Calling the split_part function:
SELECT master.dbo.split_part(lname, ',', 3) AS [extracted_string] FROM #tmp
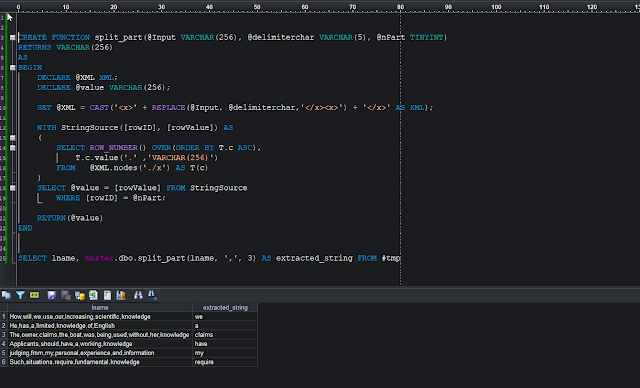 |
| Using a XML based custom function split_part |
Further reading:
STRING_SPLIT (Transact-SQL): https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/functions/string-split-transact-sql?view=sql-server-ver16 PostgreSQL: String Functions and Operators: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/functions-string.html



